2025
REaMA: Building Biomedical Relation Extraction Specialized Large Language Models Through Instruction Tuning.
Zhang, Y.-D., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.#, He, Z.-N.#, Yen, Gary G. (# corresponding author)
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2025
Biomedical relation extraction (BioRE) is key for extracting semantic relations from biomedical texts, but general large language models (LLMs) like WizardLM-70B and LLaMA-2-70B perform poorly, with low F-scores (14.05 and 12.21) compared to the state-of-the-art (65.17) on the BioRED dataset. A new multitask instruction-tuning framework, using a curated dataset called REInstruct with 150,000 instruction-response pairs, transforms general LLMs into BioRE-specialized models named REaMA (7B and 13B sizes). REaMA models show strong performance across seven BioRE datasets, with REaMA-2-13B surpassing the state-of-the-art on five datasets. Adding chain-of-thought (CoT) to REInstruct further boosts REaMA’s generalization.
REaMA: Building Biomedical Relation Extraction Specialized Large Language Models Through Instruction Tuning.
Zhang, Y.-D., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.#, He, Z.-N.#, Yen, Gary G. (# corresponding author)
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2025
Biomedical relation extraction (BioRE) is key for extracting semantic relations from biomedical texts, but general large language models (LLMs) like WizardLM-70B and LLaMA-2-70B perform poorly, with low F-scores (14.05 and 12.21) compared to the state-of-the-art (65.17) on the BioRED dataset. A new multitask instruction-tuning framework, using a curated dataset called REInstruct with 150,000 instruction-response pairs, transforms general LLMs into BioRE-specialized models named REaMA (7B and 13B sizes). REaMA models show strong performance across seven BioRE datasets, with REaMA-2-13B surpassing the state-of-the-art on five datasets. Adding chain-of-thought (CoT) to REInstruct further boosts REaMA’s generalization.
Pharmacophore-Oriented 3D Molecular Generation towards Efficient Feature-Customized Drug Discovery.
Peng, J.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Yang, Z.-B.*, Chen, Y.-T.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Nature Computational Science 2025
PhoreGen, a novel pharmacophore-oriented 3D molecular generation method, uses asynchronous updates and message-passing to integrate ligand-pharmacophore mapping, producing chemically reasonable, diverse, and drug-like molecules with high binding affinity. It successfully identified new bicyclic boronate inhibitors for metallo- and serine-β-lactamases and first-in-class covalent inhibitors for metallo-nicotinamidases, demonstrating its potential for feature-customized drug discovery.
Pharmacophore-Oriented 3D Molecular Generation towards Efficient Feature-Customized Drug Discovery.
Peng, J.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Yang, Z.-B.*, Chen, Y.-T.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Nature Computational Science 2025
PhoreGen, a novel pharmacophore-oriented 3D molecular generation method, uses asynchronous updates and message-passing to integrate ligand-pharmacophore mapping, producing chemically reasonable, diverse, and drug-like molecules with high binding affinity. It successfully identified new bicyclic boronate inhibitors for metallo- and serine-β-lactamases and first-in-class covalent inhibitors for metallo-nicotinamidases, demonstrating its potential for feature-customized drug discovery.
VenusMutHub-A benchmark for protein mutation effect prediction
Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2025
Highlight on VenusMutHub.
VenusMutHub-A benchmark for protein mutation effect prediction
Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2025
Highlight on VenusMutHub.
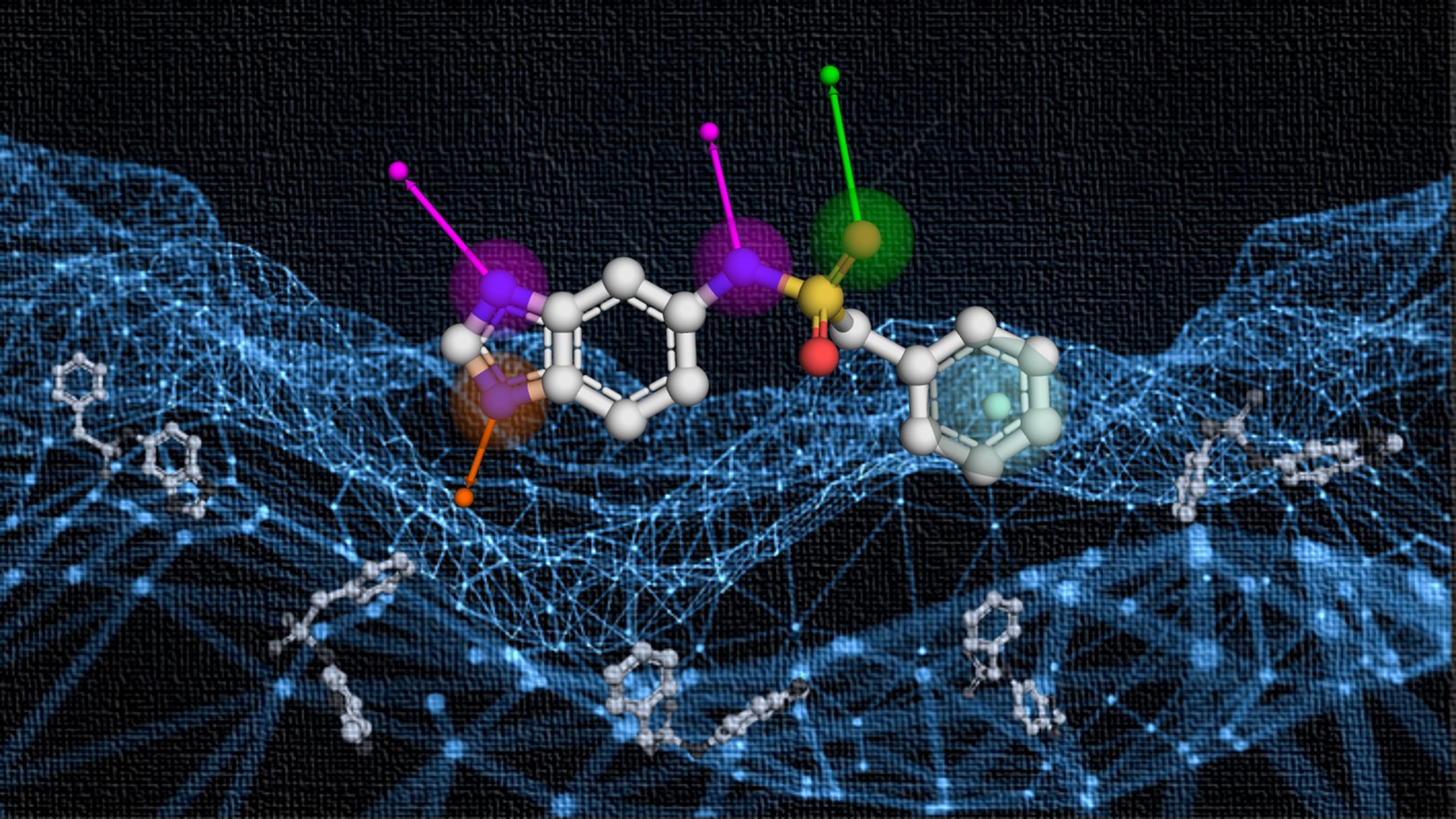
Knowledge-Guided Diffusion Model for 3D Ligand-Pharmacophore Mapping.
Yu, J.-L., Zhou, C., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Nature Communications 2025
A knowledge-guided diffusion framework for ‘on-the-fly’ 3D ligand-pharmacophore mapping, named DiffPhore, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting ligand binding conformations, surpassing traditional pharmacophore tools and several advanced docking methods.
Knowledge-Guided Diffusion Model for 3D Ligand-Pharmacophore Mapping.
Yu, J.-L., Zhou, C., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Nature Communications 2025
A knowledge-guided diffusion framework for ‘on-the-fly’ 3D ligand-pharmacophore mapping, named DiffPhore, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting ligand binding conformations, surpassing traditional pharmacophore tools and several advanced docking methods.
2024
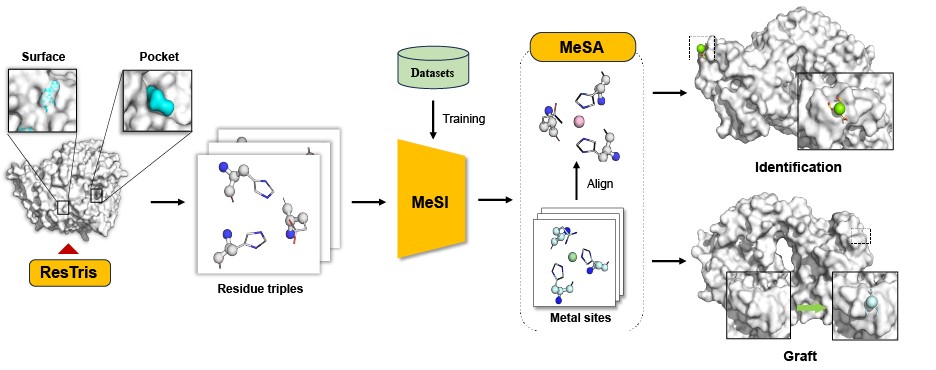
Geometric deep learning-enabled metal-binding site identification and grafting.
Yu, J.-L.*, Wang, Y.-G., Peng, J., Wu, J.-W., Zhou, C., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Fundamental Research 2024
MeSiteIG, a geometric deep learning tool, enables metal-binding site identification and grafting using E3-equivariant graph neural networks, achieving high accuracy and speed (~300 samples/second) in predicting metal-binding residues, identifying overlooked protein metal-binding sites, and designing novel metalloproteins by grafting metal sites onto antibodies and protein pockets.
Geometric deep learning-enabled metal-binding site identification and grafting.
Yu, J.-L.*, Wang, Y.-G., Peng, J., Wu, J.-W., Zhou, C., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Fundamental Research 2024
MeSiteIG, a geometric deep learning tool, enables metal-binding site identification and grafting using E3-equivariant graph neural networks, achieving high accuracy and speed (~300 samples/second) in predicting metal-binding residues, identifying overlooked protein metal-binding sites, and designing novel metalloproteins by grafting metal sites onto antibodies and protein pockets.
TarKG: A Comprehensive Biomedical Knowledge Graph for Target Discovery.
Zhou, C., Cai, C.-P., Huang, X.-T., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Bioinformatics 2024
Comprehensive biomedical KG focusing on target discovery, termed TarKG, is established by integrating seven existing biomedical KGs, nine public databases, and traditional Chinese medicine knowledge databases and providing a user-friendly web server that enables users to perform knowledge retrieval and relation inference using TarKG.
TarKG: A Comprehensive Biomedical Knowledge Graph for Target Discovery.
Zhou, C., Cai, C.-P., Huang, X.-T., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Bioinformatics 2024
Comprehensive biomedical KG focusing on target discovery, termed TarKG, is established by integrating seven existing biomedical KGs, nine public databases, and traditional Chinese medicine knowledge databases and providing a user-friendly web server that enables users to perform knowledge retrieval and relation inference using TarKG.
2023
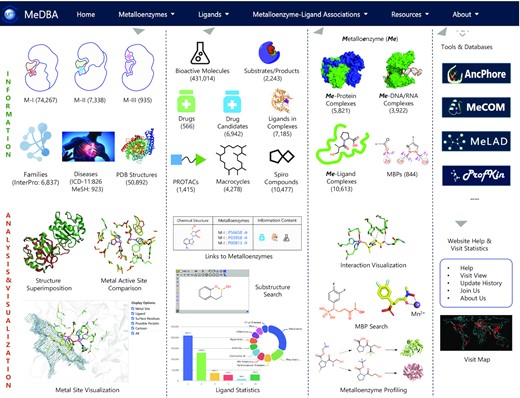
MeDBA: the Metalloenzyme Data Bank and Analysis Platform.
Yu, J.-L.*, Wu, S.*, Zhou, C., Dai, Q.-Q., Schofield, Christopher J., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Nucleic Acids Research 2023
This work has expanded the scope of metalloenzyme-specific knowledge and services, by forming a versatile platform, termed the Metalloenzyme Data Bank and Analysis (MeDBA), which provides comprehensive information on metaloenzyme activities, expression profiles, family and disease links.
MeDBA: the Metalloenzyme Data Bank and Analysis Platform.
Yu, J.-L.*, Wu, S.*, Zhou, C., Dai, Q.-Q., Schofield, Christopher J., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Nucleic Acids Research 2023
This work has expanded the scope of metalloenzyme-specific knowledge and services, by forming a versatile platform, termed the Metalloenzyme Data Bank and Analysis (MeDBA), which provides comprehensive information on metaloenzyme activities, expression profiles, family and disease links.
2022
Advances in Computer-aided Metalloenzyme-targeted Drug Discovery.
Yu, J.-L.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy 2022
This review explores the use of metal-binding pharmacophores, structure-based drug design, and AI strategies in targeting metalloenzymes-key drug targets due to their role in physiological and pathological processes-highlighting progress, advantages, and challenges in addressing the complex, dynamic electronic and geometric properties of metal-binding sites.
Advances in Computer-aided Metalloenzyme-targeted Drug Discovery.
Yu, J.-L.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy 2022
This review explores the use of metal-binding pharmacophores, structure-based drug design, and AI strategies in targeting metalloenzymes-key drug targets due to their role in physiological and pathological processes-highlighting progress, advantages, and challenges in addressing the complex, dynamic electronic and geometric properties of metal-binding sites.
Deep learning in target prediction and drug repositioning: recent advances and challenges.
Yu, J.-L.*, Dai, Q.-Q.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Drug Discovery Today 2022
This review details the advancements and applications of deep learning in innovative drug discovery, covering protein structure prediction, drug target prediction, drug-target interaction prediction, drug synthesis route design, de novo drug design, and ADMET prediction, while summarizing current challenges and potential solutions to guide future development.
Deep learning in target prediction and drug repositioning: recent advances and challenges.
Yu, J.-L.*, Dai, Q.-Q.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Drug Discovery Today 2022
This review details the advancements and applications of deep learning in innovative drug discovery, covering protein structure prediction, drug target prediction, drug-target interaction prediction, drug synthesis route design, de novo drug design, and ADMET prediction, while summarizing current challenges and potential solutions to guide future development.
Recent Advances in Deep Learning Aided Drug Discovery.
Dai, Q.-Q.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Progress in Pharmaceutical Sciences 2022
This review details the advancements and applications of deep learning in innovative drug discovery, covering protein structure prediction, drug target prediction, drug-target interaction prediction, drug synthesis route design, de novo drug design, and ADMET prediction, while summarizing current challenges and potential solutions to guide future development.
Recent Advances in Deep Learning Aided Drug Discovery.
Dai, Q.-Q.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Progress in Pharmaceutical Sciences 2022
This review details the advancements and applications of deep learning in innovative drug discovery, covering protein structure prediction, drug target prediction, drug-target interaction prediction, drug synthesis route design, de novo drug design, and ADMET prediction, while summarizing current challenges and potential solutions to guide future development.
2021
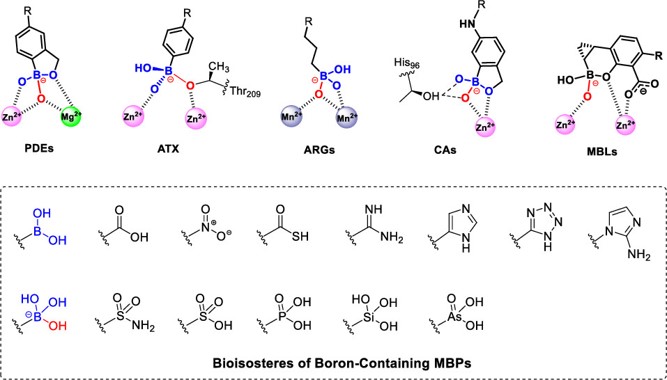
Targeting Metalloenzymes by Boron-Containing Metal-Binding Pharmacophores.
Xiao, Y.-C.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Dai, Q.-Q., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021
This Perspective focuses on boron-containing MBPs, which display unique binding modes with metalloenzyme active sites, particularly via mimicking native substrates or tetrahedral transition states, which make exploitation of metal-binding pharmacophores critical to inhibitor development targeting meetalloenzymes.
Targeting Metalloenzymes by Boron-Containing Metal-Binding Pharmacophores.
Xiao, Y.-C.*, Yu, J.-L.*, Dai, Q.-Q., Li, G.-B.# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021
This Perspective focuses on boron-containing MBPs, which display unique binding modes with metalloenzyme active sites, particularly via mimicking native substrates or tetrahedral transition states, which make exploitation of metal-binding pharmacophores critical to inhibitor development targeting meetalloenzymes.
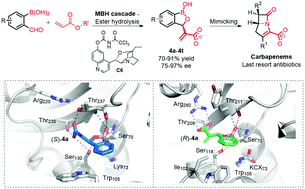
Design and enantioselective synthesis of 3-(α-acrylic acid) benzoxaboroles to combat carbapenemase resistance.
Xiao, Y.-C., Chen, X.-P., Deng, J., Yan, Y.-H., Zhu, K.-R., Li, G., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Chemical Communications 2021
Crystallographic analyses validate the proposed mechanism of binding to carbapenemases, i.e. in a manner relating to their antibiotic substrates, and illustrate how combining a structure-based design approach with asymmetric catalysis can efficiently lead to potent β-lactamase inhibitors.
Design and enantioselective synthesis of 3-(α-acrylic acid) benzoxaboroles to combat carbapenemase resistance.
Xiao, Y.-C., Chen, X.-P., Deng, J., Yan, Y.-H., Zhu, K.-R., Li, G., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Chemical Communications 2021
Crystallographic analyses validate the proposed mechanism of binding to carbapenemases, i.e. in a manner relating to their antibiotic substrates, and illustrate how combining a structure-based design approach with asymmetric catalysis can efficiently lead to potent β-lactamase inhibitors.
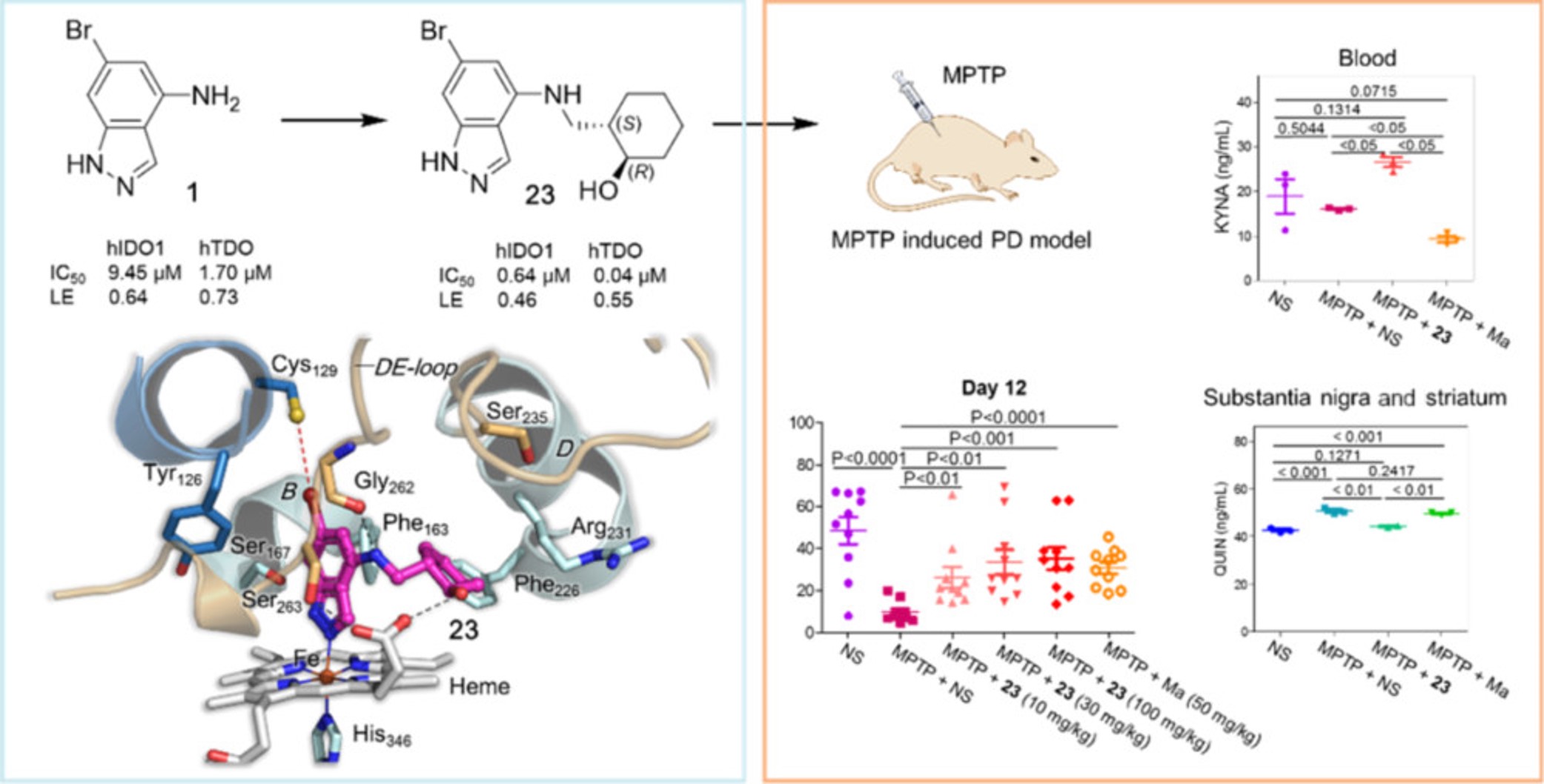
X-ray Structure-Guided Discovery of a Potent, Orally Bioavailable, Dual Human Indoleamine/Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase (hIDO/hTDO) Inhibitor That Shows Activity in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.
Ning, X.-L., Li, Y.-Z., Huo, C., Deng, J., Gao, C., Zhu, K.-R., Wu, Y.-X., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021
Biochemical, biophysical, and computational analyses reveal that 1H-indazole-4-amines inhibit both hIDO1 and hTDO by a mechanism involving direct coordination with the heme ferrous and ferric states, and likely has specific anti-PD mechanisms.
X-ray Structure-Guided Discovery of a Potent, Orally Bioavailable, Dual Human Indoleamine/Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase (hIDO/hTDO) Inhibitor That Shows Activity in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.
Ning, X.-L., Li, Y.-Z., Huo, C., Deng, J., Gao, C., Zhu, K.-R., Wu, Y.-X., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021
Biochemical, biophysical, and computational analyses reveal that 1H-indazole-4-amines inhibit both hIDO1 and hTDO by a mechanism involving direct coordination with the heme ferrous and ferric states, and likely has specific anti-PD mechanisms.

Discovery of 3-Aryl Substituted Benzoxaboroles as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Serine- and Metallo-β-Lactamases.
Yan, Y.-H., Li, Z.-F., Ning, X.-L., Deng, J., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2021
A series of 3-aryl substituted benzoxaborole derivatives were developed as broad-spectrum inhibitors of serine- and metallo-β-lactamases, with compound 9f showing potent inhibition (IC50 of 86 nM for KPC-2) and significantly reducing meropenem MICs in resistant bacterial strains without toxicity in HEK293T cells.
Discovery of 3-Aryl Substituted Benzoxaboroles as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Serine- and Metallo-β-Lactamases.
Yan, Y.-H., Li, Z.-F., Ning, X.-L., Deng, J., Yu, J.-L., Li, G.-B.# (# corresponding author)
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2021
A series of 3-aryl substituted benzoxaborole derivatives were developed as broad-spectrum inhibitors of serine- and metallo-β-lactamases, with compound 9f showing potent inhibition (IC50 of 86 nM for KPC-2) and significantly reducing meropenem MICs in resistant bacterial strains without toxicity in HEK293T cells.